北京建设监督网站上海做高端网站建设
Elasticsearch 概念
入门学习:
- Index索引=>MySQL 里的表(table)
- 建表、增删改查(查询需要花费的学习时间最多)
- 用客户端去调用 ElasticSearch(3 种)
- 语法:SQL、代码的方法(4 种语法)
ES 相比于 MySQL,能够自动帮我们做分词,能够非常高效、灵活地查询内容。
索引(倒排索引)
正向索引:理解为书籍的目录,可以快速帮你找到对应的内容(怎么根据页码找到文章)
倒排索引:怎么根据内容找到文章
文章 A: 你好,我是 rapper
文章 B: 苏麟暴打小杨科
切词 :
| 词 | id |
| 你好 | 文章 A |
| 我 | 文章 A |
| rapper | 文章 A |
| 苏麟 | 文章 B |
| 暴打 | 文章 B |
| 杨科 | 文章 B |
用户搜索 : 苏麟杨科
ES切词 : 苏麟 , 杨科
然后去倒排索引表找对应的文章
ES 的几种调用方式
1) restful api 调用(http 请求)
GET请求 : localhost:9200
curl 可以模拟发送请求: curl -XGET"localhost:9200/?pretty
ES 的启动端口
1.9200:给外部用户(给客户端调用)的端口
2.9300:给 ES 集群内部通信的(外部调用不了的)
2) kibana devtools
自由地对 ES 进行操作(本质也是 restful api)
devtools 不建议生产环境使用
3)客户端调用
java 客户端、go 客户端等。
参考文档 : Getting started | Elasticsearch Java API Client [7.17] | Elastic
ES 的语法
DSL
json 格式,好理解;和 http 请求最兼容,应用最广
建表,插入数据 (文档就是MySQL里的表,映射就是MySQL里的字段)
post 就相当于表名 , title 和 content 就相当于字段
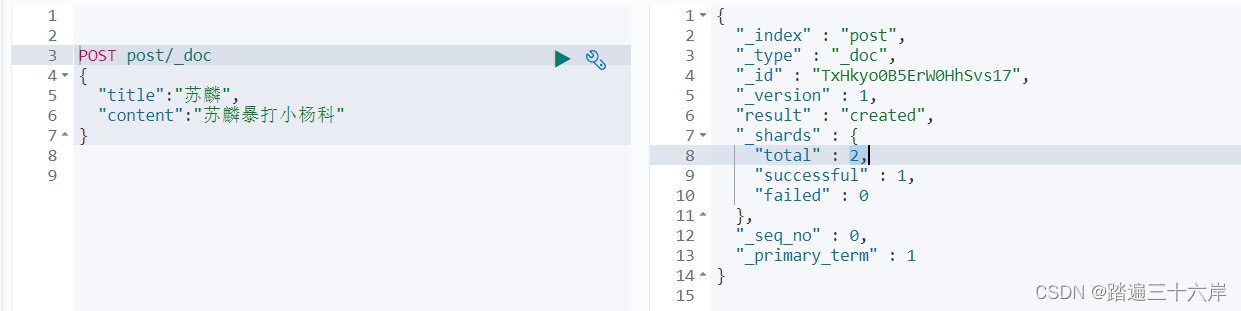
POST post/_doc
{"title":"苏麟","content":"苏麟暴打小杨科"
}有 successful 就代表存入成功了
查询
DSL (不要背) : Query DSL | Elasticsearch Guide [7.17] | Elastic
查询全部
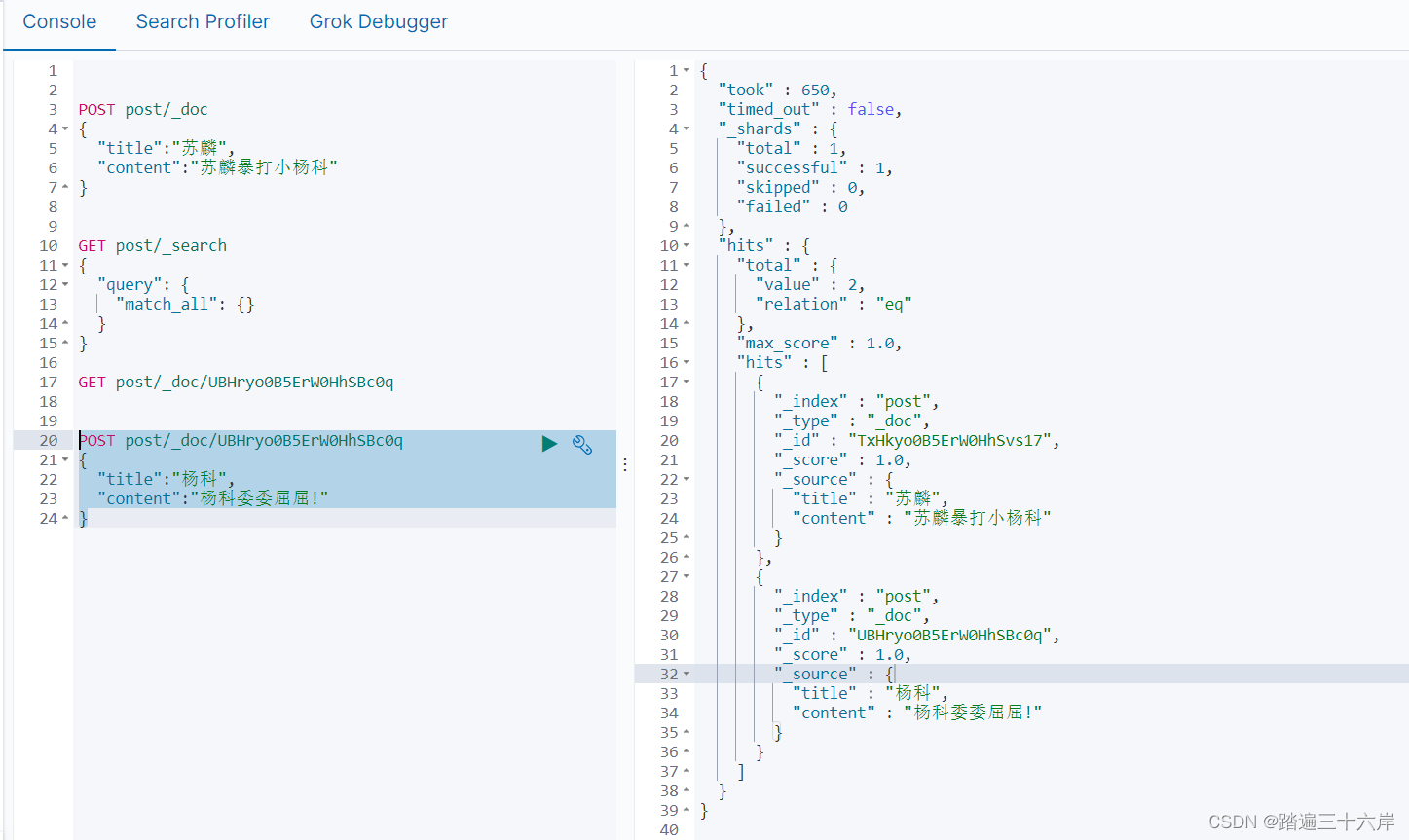
GET post/_search
{"query": {"match_all": {}}
}
根据 id 查询
GET post/_doc/UBHryo0B5ErW0HhSBc0q

修改
根据 id 修改
POST post/_doc/UBHryo0B5ErW0HhSBc0q
{"title":"杨科","content":"杨科委委屈屈!"
}
删除
根据文档删除
DELETE post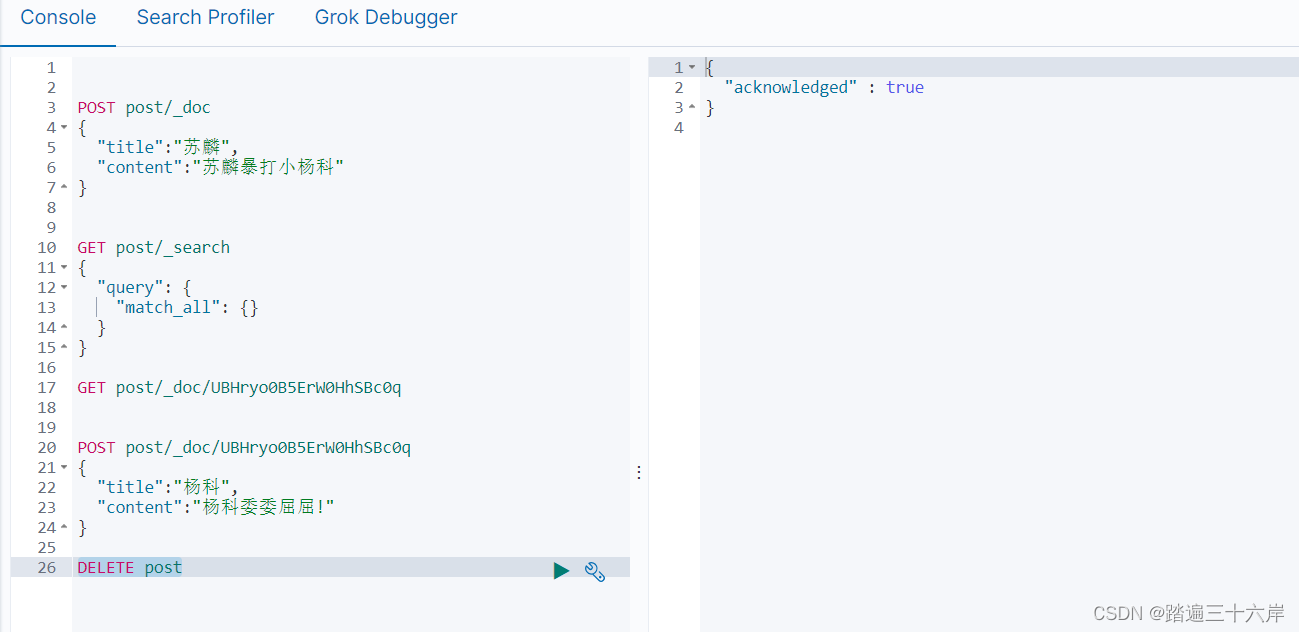
EQL
专门查询 ECS 文档(标准指标文档)的数据的语法,更加规范,但只适用于特定场景(比如事件流)
文档 : EQL search | Elasticsearch Guide [7.17] | Elastic
建表,插入
POST post_my/_doc
{"title": "苏麟爱看美女","@timestamp": "2099-05-06T16:21:15.000Z","event": {"original": "192.0.2.42 - - [06/May/2099:16:21:15 +0000] \"GET /images/bg.jpg HTTP/1.0\" 200 24736"}
}查询
GET post_my/_search
{"query": {"match_all": { }},"sort": [{"@timestamp": "desc"}]
}
SQL
文档 : Getting Started with SQL | Elasticsearch Guide [7.17] | Elastic
查询
POST /_sql?format=txt
{"query": "SELECT * FROM post "
}
Painless Scripting language
编程式取值,更灵活,但是学习成本高
Mapping
文档 : Explicit mapping | Elasticsearch Guide [7.17] | Elastic
可以理解为数据库的表结构,有哪些字段、字段类型,
ES 支持动态 mapping,表结构可以动态改变,而不像 MySQL 一样必须手动建表,没有的字段就不能插入。
GET user/_mappingPUT /user
{"mappings": {"properties": {"age": { "type": "integer" }, "email": { "type": "keyword" }, "name": { "type": "text" } }}
}分词器
指定了分词的规则。
内置分词器 : Built-in analyzer reference | Elasticsearch Guide [7.17] | Elastic
示例 :
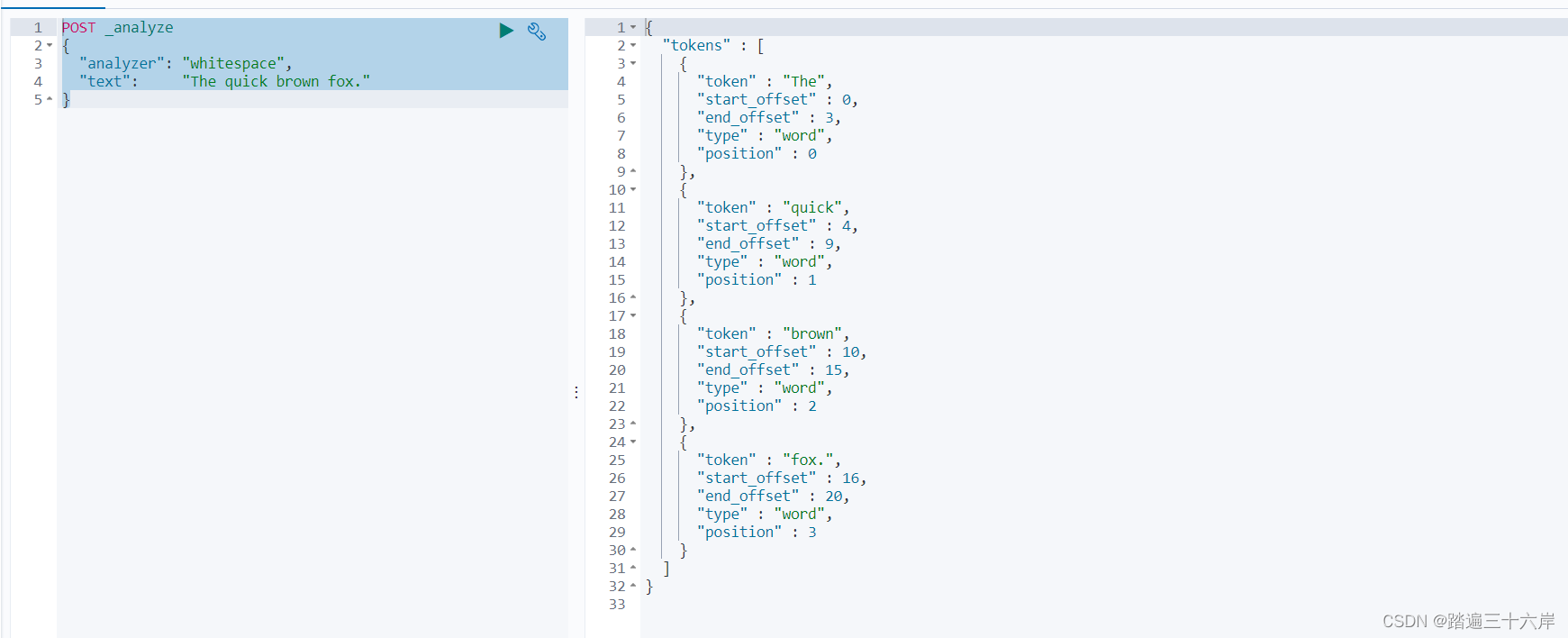
空格分词器: whitespace,结果The、quick、brown、fox.
POST _analyze
{"analyzer": "whitespace","text": "The quick brown fox."
}
标准分词规则,结果:is、this、deja、vu
POST _analyze
{"tokenizer": "standard","filter": [ "lowercase", "asciifolding" ],"text": "Is this déja vu?"
}
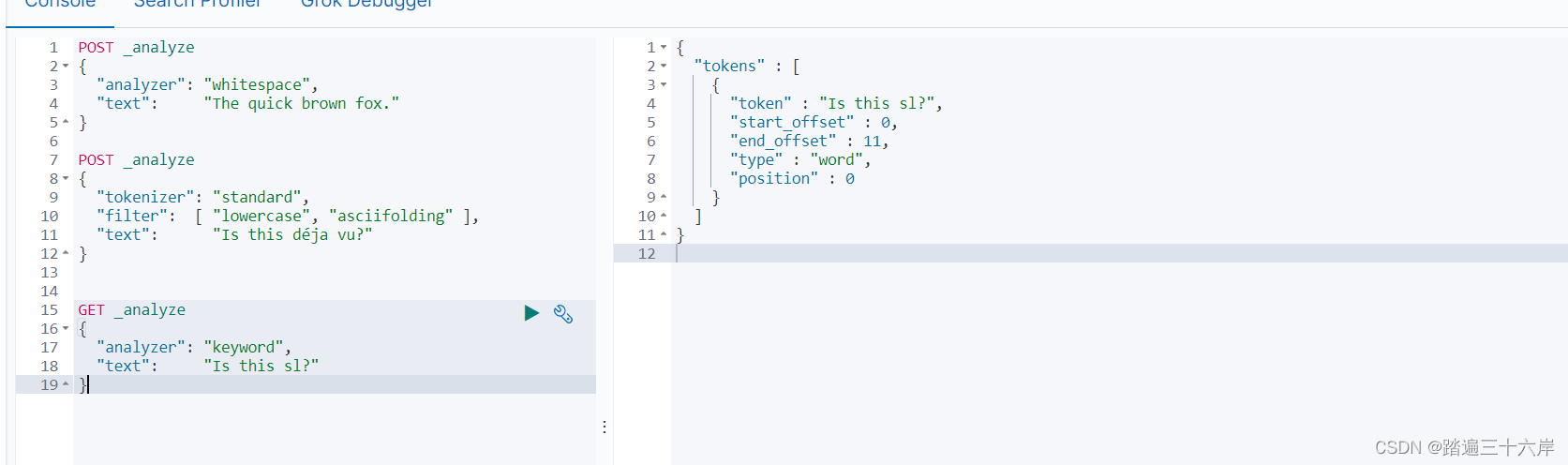
关键词分词器:就是不分词,整句话当作专业术语
GET _analyze
{"analyzer": "keyword", "text": "Is this sl?"
}
打分机制
比如有3条内容:
1.苏麟是gay
2.苏麟暴打小杨科
3.小杨科
用户搜索:
1.杨科,第三条分数最高,因为第三条匹配了关键词,而且更短(匹配比例更大)
2.苏麟 => 苏麟是gay => 苏麟暴打小杨科 , 排序结果 1 2
参考文章 : Controlling Relevance | Elasticsearch: The Definitive Guide [master] | Elastic
Java 操作 ES
3 种方式:
1) ES 官方的 Java API
文章 : Introduction | Elasticsearch Java API Client [7.17] | Elastic
快速开始 : Connecting | Elasticsearch Java API Client [7.17] | Elastic
2) ES 以前的官方 Java APl,HighLevelRestclient(已废弃,不建议用)
3) Spring Data Elasticsearch(推荐)
spring-data 系列:spring 提供的操作数据的框架
spring-data-redis:操作 redis 的-套方法
spring-data-mongodb:操作 mongodb 的一套方法
spring-data-elasticsearch:操作 elasticsearch 的一套方法
...
建表结构:
aliases 起别名
PUT post_v1
{"aliases": {"post": {}},"mappings": {"properties": {"title": {"type": "text","analyzer": "ik_max_word","search_analyzer": "ik_smart","fields": {"keyword": {"type": "keyword","ignore_above": 256}}},"content": {"type": "text","analyzer": "ik_max_word","search_analyzer": "ik_smart","fields": {"keyword": {"type": "keyword","ignore_above": 256}}},"tags": {"type": "keyword"},"thumbNum": {"type": "long"},"favourNum": {"type": "long"},"userId": {"type": "keyword"},"createTime": {"type": "date"},"updateTime": {"type": "date"},"isDelete": {"type": "keyword"}}}
}增删改查
第一种方式: ElasticsearchRepository<xxxx, Long>,默认提供了简单的增删改查,多用于可预期的、相对没那么复杂的查询、自定义查询,返回结果相对简单直接。
有一些现成的方法可以使用
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//package org.springframework.data.repository;import java.util.Optional;@NoRepositoryBean
public interface CrudRepository<T, ID> extends Repository<T, ID> {<S extends T> S save(S entity);<S extends T> Iterable<S> saveAll(Iterable<S> entities);Optional<T> findById(ID id);boolean existsById(ID id);Iterable<T> findAll();Iterable<T> findAllById(Iterable<ID> ids);long count();void deleteById(ID id);void delete(T entity);void deleteAllById(Iterable<? extends ID> ids);void deleteAll(Iterable<? extends T> entities);void deleteAll();
}
第二种方式: Spring 默认给我们提供的操作 es 的客户端对象 ElasticsearchRestTemplate,也提供了增删改查它的增删改查更灵活,适用于更复杂的操作,返回结果更完整,但需要自己解析。
准备工作
package com.yupi.springbootinit.model.dto.post;import cn.hutool.core.collection.CollUtil;
import cn.hutool.json.JSONUtil;
import com.yupi.springbootinit.model.entity.Post;
import lombok.Data;import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Document;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Field;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.FieldType;import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;/*** 帖子 ES 包装类***/
@Document(indexName = "post")
@Data
public class PostEsDTO implements Serializable {private static final String DATE_TIME_PATTERN = "yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSS'Z'";/*** id*/@Idprivate Long id;/*** 标题*/private String title;/*** 内容*/private String content;/*** 标签列表*/private List<String> tags;/*** 创建用户 id*/private Long userId;/*** 创建时间*/@Field(index = false, store = true, type = FieldType.Date, format = {}, pattern = DATE_TIME_PATTERN)private Date createTime;/*** 更新时间*/@Field(index = false, store = true, type = FieldType.Date, format = {}, pattern = DATE_TIME_PATTERN)private Date updateTime;/*** 是否删除*/private Integer isDelete;private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;/*** 对象转包装类** @param post* @return*/public static PostEsDTO objToDto(Post post) {if (post == null) {return null;}PostEsDTO postEsDTO = new PostEsDTO();BeanUtils.copyProperties(post, postEsDTO);String tagsStr = post.getTags();if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(tagsStr)) {postEsDTO.setTags(JSONUtil.toList(tagsStr, String.class));}return postEsDTO;}/*** 包装类转对象** @param postEsDTO* @return*/public static Post dtoToObj(PostEsDTO postEsDTO) {if (postEsDTO == null) {return null;}Post post = new Post();BeanUtils.copyProperties(postEsDTO, post);List<String> tagList = postEsDTO.getTags();if (CollUtil.isNotEmpty(tagList)) {post.setTags(JSONUtil.toJsonStr(tagList));}return post;}
}
public interface PostEsDao extends ElasticsearchRepository<PostEsDTO, Long> {}@Resourceprivate PostEsDao postEsDao;测试
@Testvoid testAdd() {PostEsDTO postEsDTO = new PostEsDTO();postEsDTO.setId(1L);postEsDTO.setTitle("苏麟");postEsDTO.setContent("风雨交加的夜晚,苏麟暴打小杨科,小杨科奄奄一息");postEsDTO.setTags(Arrays.asList("苏麟", "杨科","暴打"));postEsDTO.setUserId(1L);postEsDTO.setCreateTime(new Date());postEsDTO.setUpdateTime(new Date());postEsDTO.setIsDelete(0);postEsDao.save(postEsDTO);System.out.println(postEsDTO.getId());}DSL 查询结果
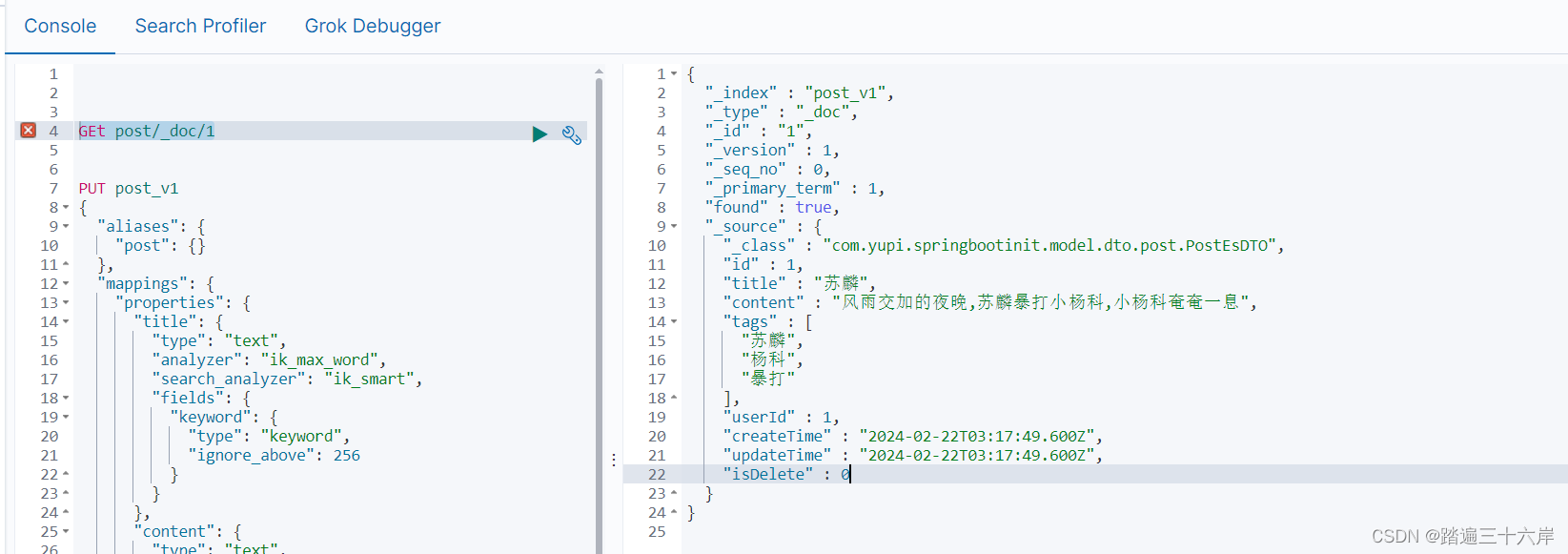
查询结果
@Testvoid testFindById() {Optional<PostEsDTO> postEsDTO = postEsDao.findById(1L);System.out.println(postEsDTO);}
DSL 查询转换 Java 代码查询
DSL 查询
文档 : Query and filter context | Elasticsearch Guide [7.17] | Elastic
文档 : Boolean query | Elasticsearch Guide [7.17] | Elastic
GET post/_search
{"query": { "bool": { //组合条件"must": [ //必须满足{ "match": { "title": "苏麟" }}, //match 模糊查询{ "match": { "content": "苏麟" }}],"filter": [ //过滤{ "term": { "status": "published" }}, //term 精确查询{ "range": { "publish_date": { "gte": "2015-01-01" }}} //范围查询]}}
}GET post/_search
{"query": { "bool": { "must": [{ "match": { "title": "苏麟" }},{ "match": { "content": "苏麟" }}]}}
}
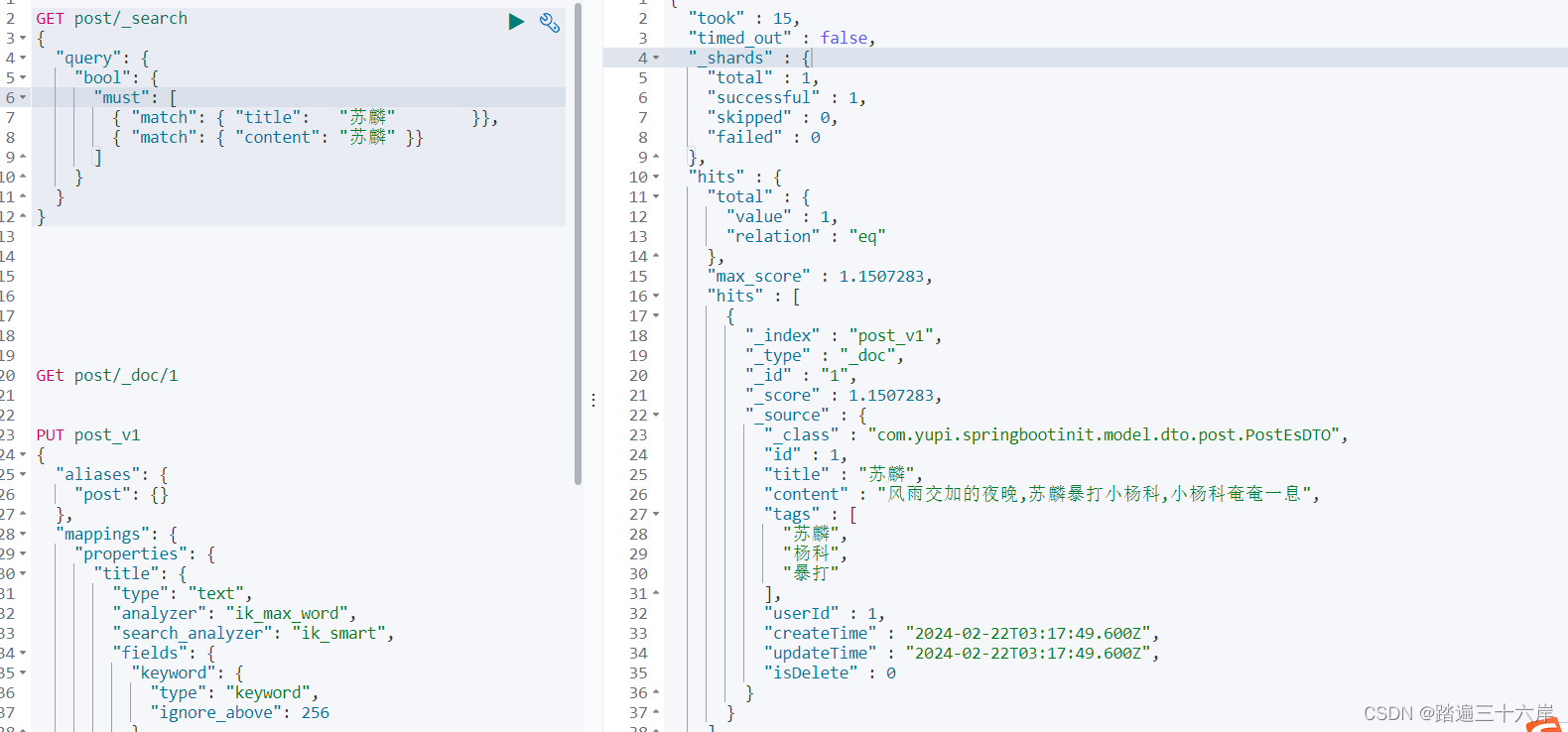
wildcard 模糊查询
regexp 正则匹配查询
查询结果中,score 代表匹配分数
建议先测试 DSL、再翻译成 Java
POST _search
{"query": {"bool" : {"must" : {"term" : { "user.id" : "kimchy" }},"filter": {"term" : { "tags" : "production" }},"must_not" : {"range" : {"age" : { "gte" : 10, "lte" : 20 }}},"should" : [{ "term" : { "tags" : "env1" } },{ "term" : { "tags" : "deployed" } }],"minimum_should_match" : 1,"boost" : 1.0}}
}这期就到这里 , 下期见 !
