网站开发进度计划企业电子商务网站的建设方式
简介
参考这篇文章:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41248872/article/details/83590337
写的比较好,这里就不赘述了。
我们在视频传输的时候,需要压缩,常见的压缩包括:
- jpeg 压缩
- h264 压缩
当然使用最多的还是 264, 毕竟他的压缩比高嘛。对于一些实时的场景比较有优势,但是这玩意还是得分不同的场合吧,如果对于带宽没限制,为了更好的画质,还是应该选 jpeg 压缩比较好。
背景
Linux下,一般的普通USB摄像头V4L2视频采集有两种方式:
- V4L2_PIX_FMT_MJPEG
- V4L2_PIX_FMT_YUYV
V4L2_PIX_FMT_MJPEG
采集方式得到的是经过MJPEG压缩的图片,图片格式是jpeg/jpg,后缀为.jpg或.jpeg。直接将采集到的.jpeg数据依序循环写入一个文件,得到的流并不能直接播放,需要封装成 avi 等视频格式才能正常播放。
V4L2_PIX_FMT_YUYV
采集方式得到的是yuyv格式的原始图像格式文件,后缀为.yuv,得到的yuv数据文件可直接利用pYUV等专业yuv格式查看器进行播放,yuv数据可经HEVC(H265)、H264、VP8、VP9等方式进行编码压缩,通过h.264压缩可得到h264码流,H264码流可直接用VLC播放器进行播放。
压缩效果对比
下面是 网友 测试得到的数据,这里只是做简单的摘录:
首先是试验条件:
统一条件:采集50帧图像(1080p分辨率、帧率5fps,视频时长10s)
然后是,对比指标:
性能对比:编码时间、压缩比、图像质量。
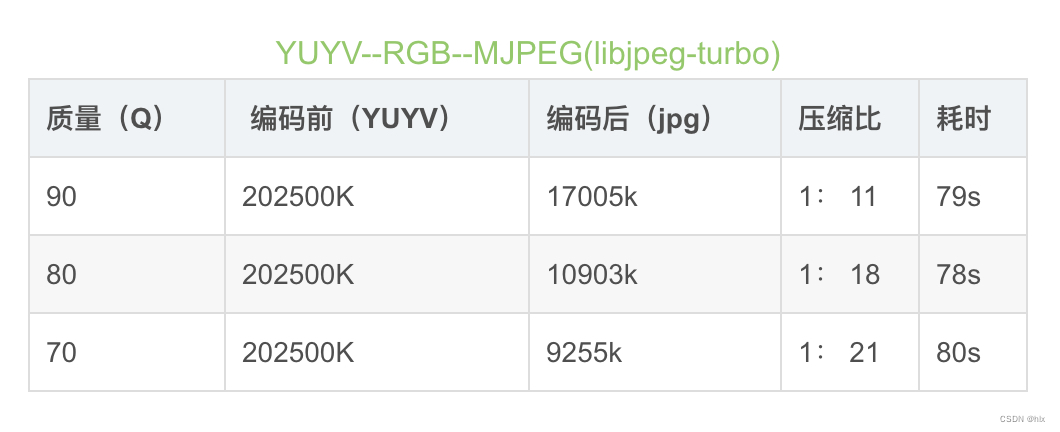
jpeg 数据
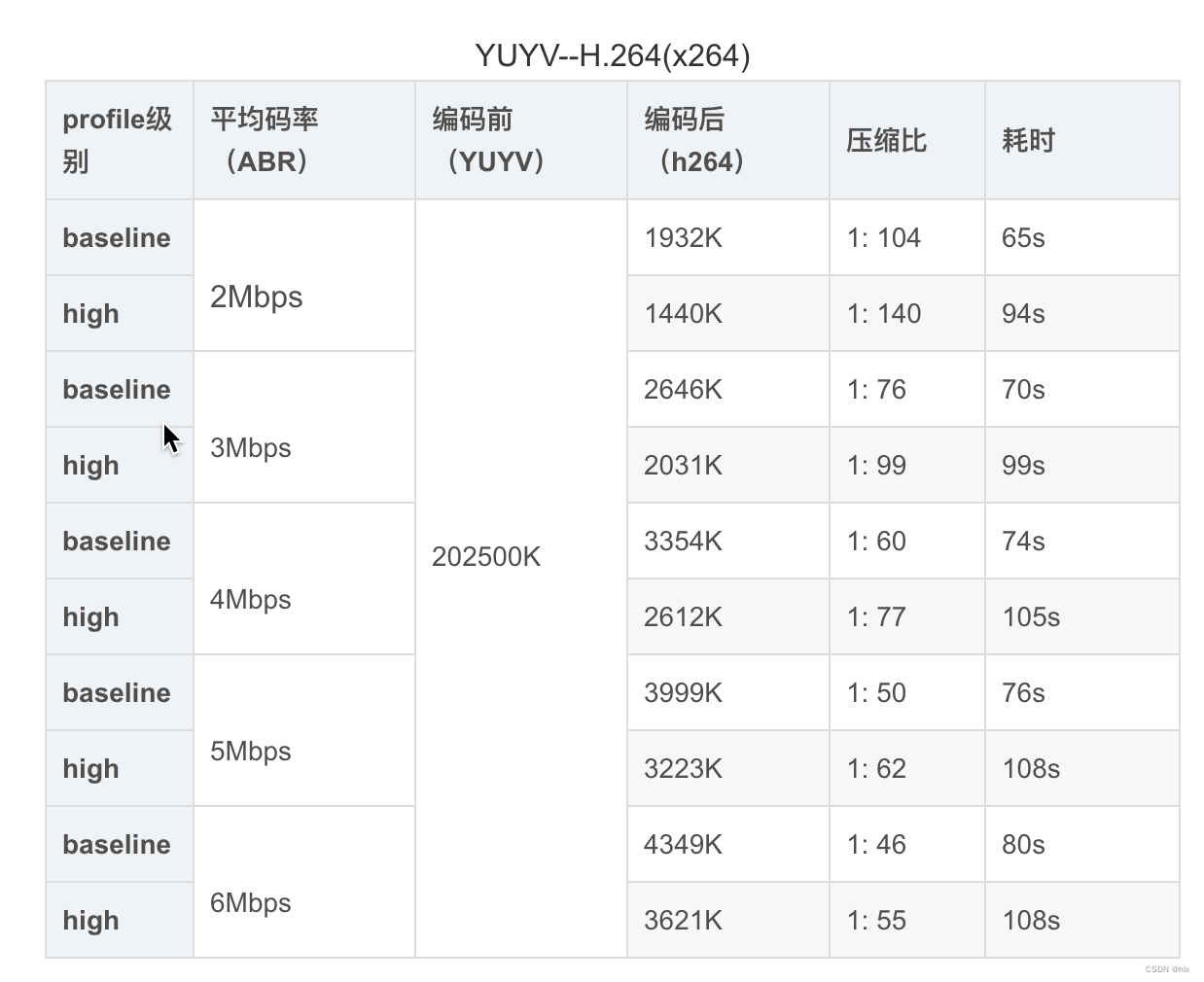
h264 数据
结论
1.就压缩率来说,H.264远远优于M-JPEG,H.264的压缩比一般能达到1:50甚至1:100以上,而M-JPEG压缩比一般小于1:20;同时由于高压缩率,经H.264压缩出的图像数据量远远小于M-JPEG,更利于实时传输,占用网络带宽更少。
2.图像质量:由于M-JPEG压缩率较小,所以能达到跟原图像接近的画质和清晰度。而H.264为了满足高压缩率,所以在图像质量上略有损失。
结语:两种压缩方式的选择最主要还是在于使用场景,合理选用。若实时性要求较高,则h.264更适合,因为数据量较小,便于传输;若对实时性要求不是很高,能接受大数据量的图像,且对图像质量要求更高的话,可考虑M-JPEG方式。
