深圳外贸商城网站建设深圳设计公司招聘信息
Python 基于 OpenCV 视觉图像处理实战 之 OpenCV 简单实战案例 之九 简单闪烁效果
目录
Python 基于 OpenCV 视觉图像处理实战 之 OpenCV 简单实战案例 之九 简单闪烁效果
一、简单介绍
二、简单闪烁效果实现原理
三、简单闪烁效果案例实现简单步骤
四、注意事项
一、简单介绍
Python是一种跨平台的计算机程序设计语言。是一种面向对象的动态类型语言,最初被设计用于编写自动化脚本(shell),随着版本的不断更新和语言新功能的添加,越多被用于独立的、大型项目的开发。Python是一种解释型脚本语言,可以应用于以下领域: Web 和 Internet开发、科学计算和统计、人工智能、教育、桌面界面开发、软件开发、后端开发、网络爬虫。
这里使用 Python 基于 OpenCV 进行视觉图像处理,......
二、简单闪烁效果实现原理
闪烁效果是指物体或光源快速、周期性地改变亮度或颜色的视觉效果。
在图像处理中,闪烁效果通常通过改变图像的亮度或对比度来实现,使图像在观察者眼中产生明暗变化的感觉。
这种效果常用于增强视觉吸引力或制造特殊效果,比如模拟闪烁的灯光、霓虹灯等。
在实际应用中,闪烁效果的频率、幅度和持续时间可以根据需要进行调整,以达到理想的视觉效果。
实现原理:
1、设定闪烁周期: 确定闪烁的周期,即图像亮度和对比度调整的时间间隔。在本例中,设定为1秒。
time.time(): 返回当前时间的时间戳,用于计算时间间隔。2、进入处理循环: 在一个无限循环中,持续处理图像以实现闪烁效果。
3、计算时间差: 在每次循环迭代中,计算当前时间与开始闪烁的时间之间的时间差。
4、调整亮度和对比度: 如果时间差大于闪烁周期,则进行图像亮度和对比度的调整。调整值通常在一定范围内随机生成,以获得随机的闪烁效果。
np.random.uniform(): 用于生成指定范围内的随机数,用于调整亮度和对比度。5、应用调整后的效果: 使用
cv2.convertScaleAbs()函数将调整后的亮度和对比度应用于原始图像,生成调整后的图像。
cv2.convertScaleAbs(): 将输入数组进行比例缩放并转换为无符号8位整数类型,用于调整图像的亮度和对比度。6、反转亮度: 如果时间差大于闪烁周期,则将调整后的图像的亮度反转,以模拟闪烁效果。
三、简单闪烁效果案例实现简单步骤
1、编写代码

2、运行效果
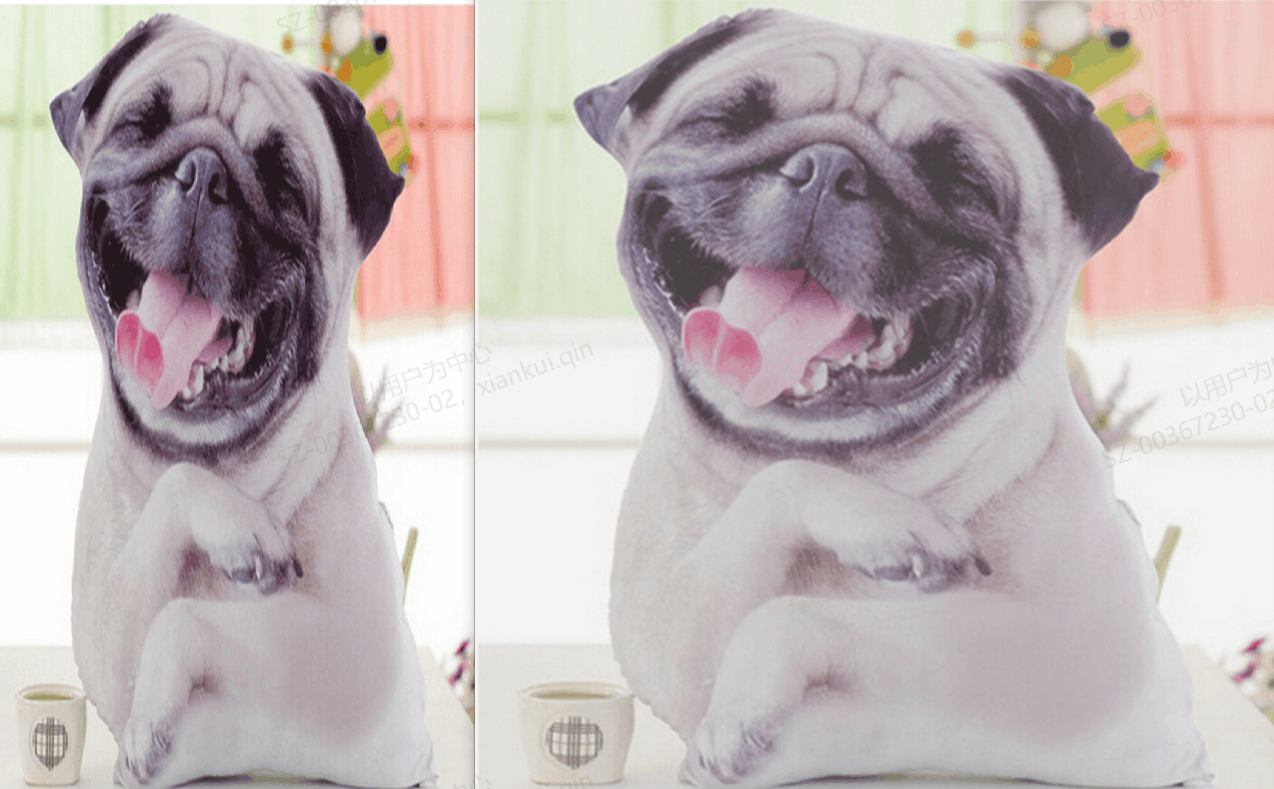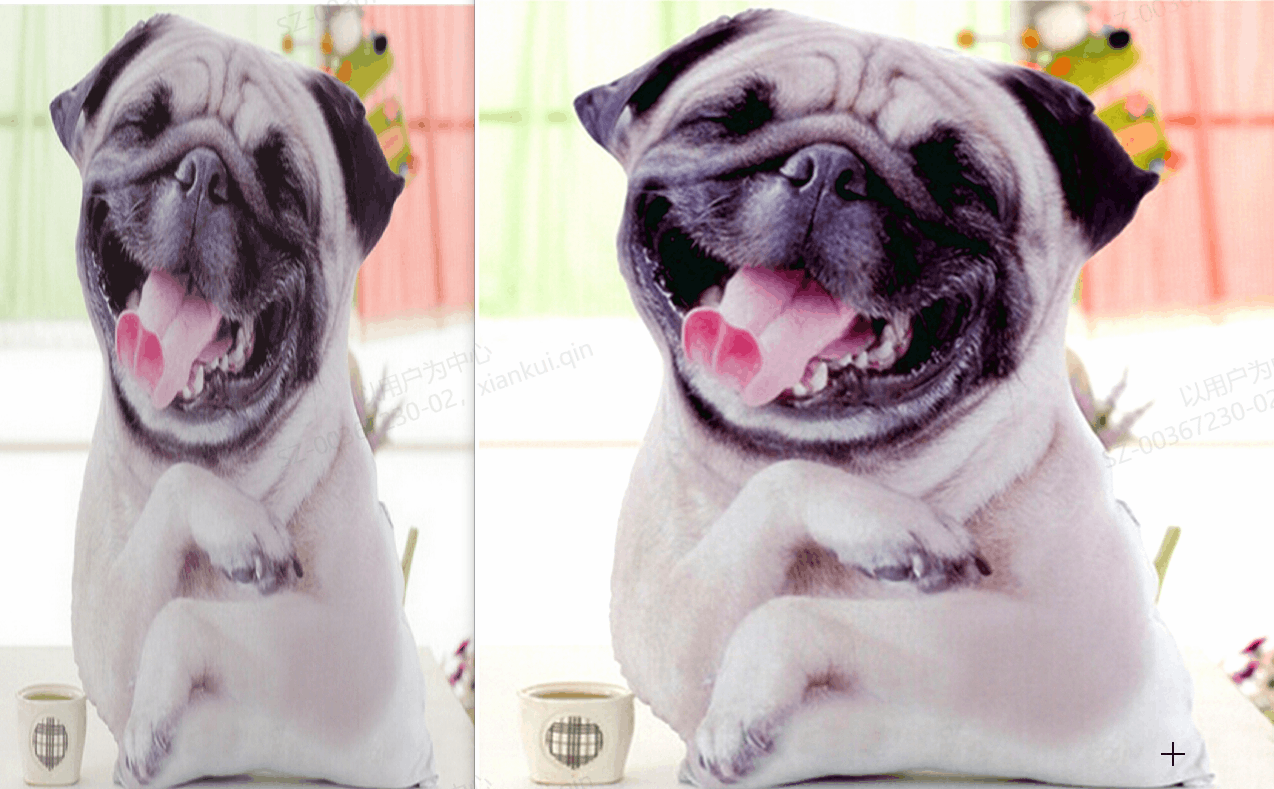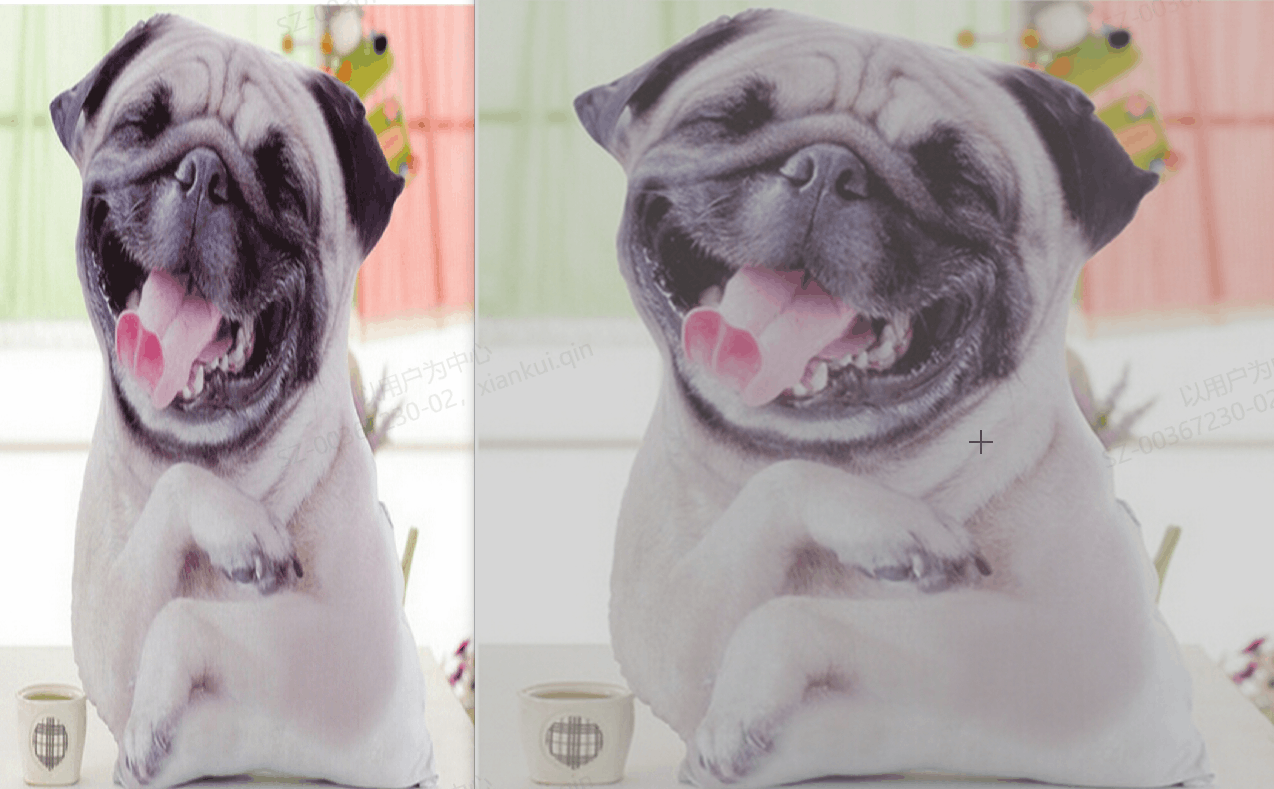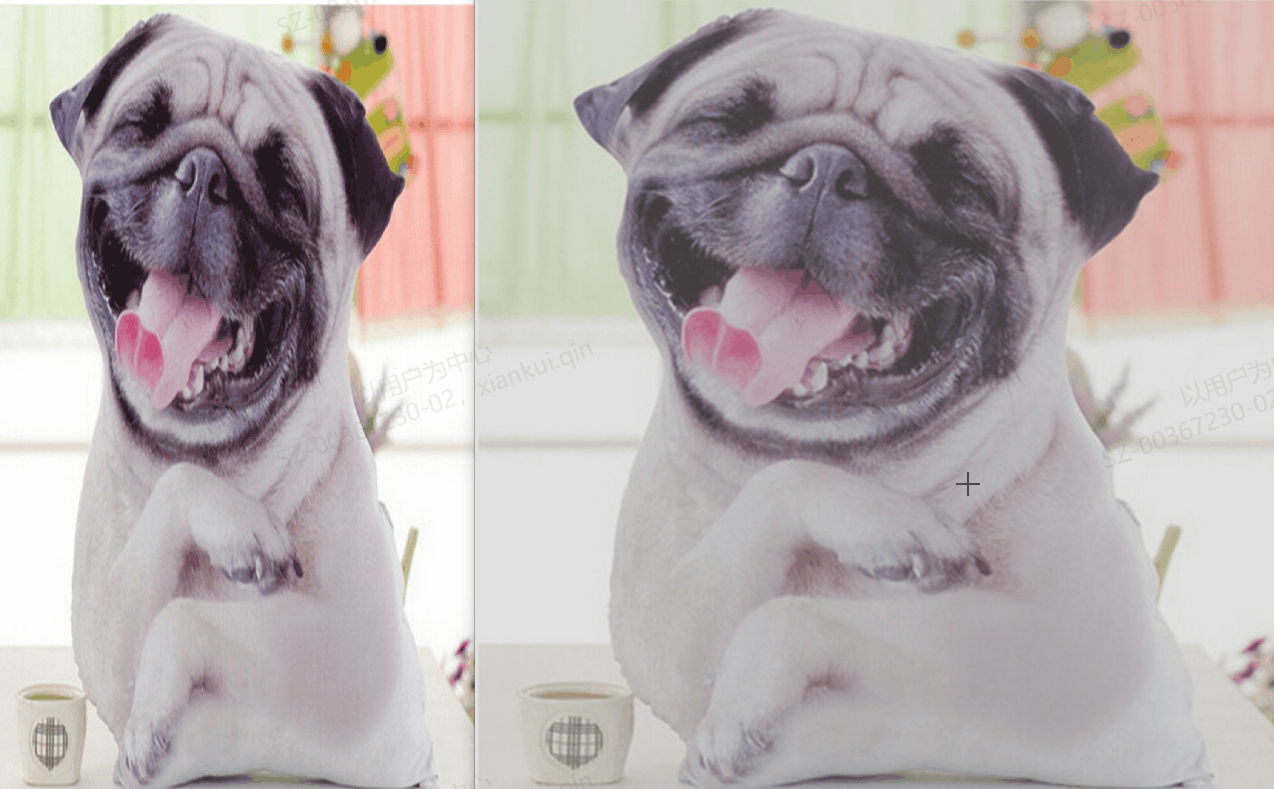
3、具体代码
"""
简单的闪烁效果1、读取图像文件: 首先,从文件系统中读取输入的图像文件,该图像将作为闪烁效果的基础。2、设定闪烁周期: 确定闪烁的周期,即图像亮度和对比度调整的时间间隔。在本例中,设定为1秒。3、进入处理循环: 在一个无限循环中,持续处理图像以实现闪烁效果。4、计算时间差: 在每次循环迭代中,计算当前时间与开始闪烁的时间之间的时间差。5、调整亮度和对比度: 如果时间差大于闪烁周期,则进行图像亮度和对比度的调整。调整值通常在一定范围内随机生成,以获得随机的闪烁效果。6、应用调整后的效果: 使用 cv2.convertScaleAbs() 函数将调整后的亮度和对比度应用于原始图像,生成调整后的图像。7、反转亮度: 如果时间差大于闪烁周期,则将调整后的图像的亮度反转,以模拟闪烁效果。8、显示处理后的图像: 使用 cv2.imshow() 函数在窗口中显示处理后的图像。9、等待用户退出: 检测用户是否按下 'q' 键,如果是则退出循环。10、释放资源: 循环结束后,释放窗口资源并结束程序。
"""import cv2
import numpy as np
import timedef BlinkingEffect(image, blink_interval=1):"""简单闪烁效果:param image::param blink_interval: 闪烁间隔时间:return:"""# 检查图像是否成功读取if image is None:print("Error: Unable to read image.")exit()# 定义闪烁周期(秒)blink_interval = blink_interval# 定义开始闪烁的时间start_blink_time = time.time()# 循环处理图像while True:# 计算当前时间和开始闪烁的时间之间的时间差current_time = time.time()time_diff = current_time - start_blink_time# 计算亮度和对比度的调整值brightness = np.random.uniform(-50, 50)contrast = np.random.uniform(0.5, 1.5)# 使用亮度和对比度调整值调整图像adjusted_image = cv2.convertScaleAbs(image, alpha=contrast, beta=brightness)# 如果时间差大于闪烁周期,则进行图像闪烁处理if time_diff > blink_interval:# 反转图像亮度adjusted_image = 255 - adjusted_image# 更新开始闪烁的时间start_blink_time = current_time# 设置窗口属性,并显示图片cv2.namedWindow("Dog", cv2.WINDOW_KEEPRATIO)cv2.imshow('Neon Light', adjusted_image)# 按下 q 键,退出if cv2.waitKey(25) & 0xFF == ord('q'):break# 释放窗口cv2.destroyAllWindows()def main():# 读取图像文件image = cv2.imread('Images/DogFace.jpg')# 设置窗口属性,并显示图片cv2.namedWindow("Dog", cv2.WINDOW_KEEPRATIO)cv2.imshow("Dog", image)# 调用闪烁效果BlinkingEffect(image, 1)if __name__ == "__main__":main()
四、注意事项
- 使用
cv2.imread()读取图像时,确保图像文件路径正确,并且图像文件存在。 - 在调整图像亮度和对比度时,可以使用
cv2.convertScaleAbs()函数来实现。亮度和对比度的调整值可以根据需要进行调整,以获得理想的闪烁效果。 - 确保在循环中正确计算时间差,并根据闪烁周期来控制图像的闪烁频率。
- 在调试代码时,可以适当调整闪烁周期和调整值,以获得更好的效果。
