图文消息点击进去是自己的网站seo自动优化软件下载
常用压缩格式: .zip .zg .bz2 .tar.gz .tar.bz2
.zip格式压缩
zip 压缩文件名 源文件
#压缩文件

注:压缩文件名写.zip后缀是为了标记该文件的压缩类型,方便管理。

注:在压缩时有压缩格式转换,所以当源文件很小时,压缩文件比源文件大。
zip -r 压缩文件名 源目录
#压缩目录
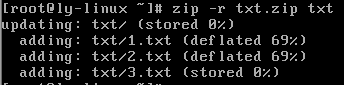
注:如果在压缩目录没有加-r指令,压缩的是一个空目录,而不包含目录下的文件。
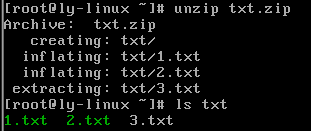
.zip格式解压缩
unzip 压缩文件
#解压缩.zip文件
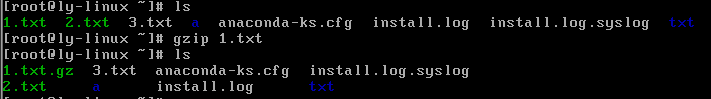
.gz格式压缩
.gzip 源文件
#压缩为.gz格式的压缩文件,源文件会消失
.gzip -c 源文件 > 压缩文件
#压缩为.gz格式,源文件保留
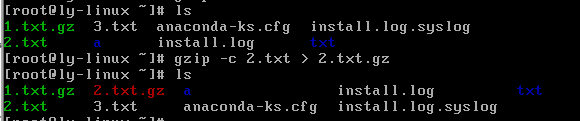
注:-c是将压缩的格式不写入新文件,打印到屏幕上,利用输出重定向造成一个既压缩.gz格式源文件也不消失的现象。但是gzip本身是不支持保留源文件压缩的。
.gzip -r 目录
#压缩目录下所有子文件,但是不能压缩目录
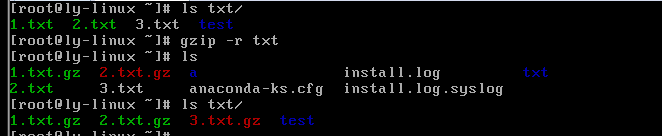
.gz格式解压缩
gzip -d 压缩文件
#解压缩文件
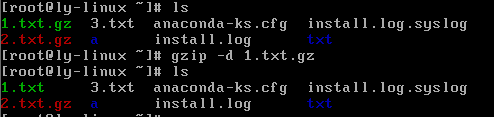
gunzip 压缩文件
#解压缩文件
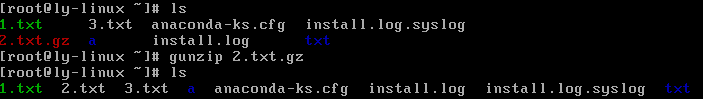
注:在解压缩目录时,加-r
.bz2格式压缩(不支持压缩目录)
bzip2 源文件
#压缩为.bz2格式,不保留源文件
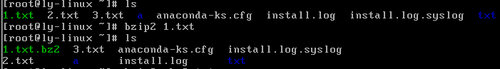
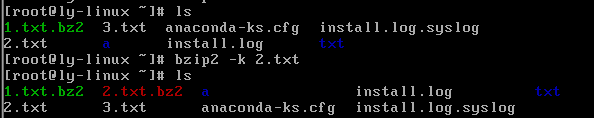
bzip2 -k 源文件
#压缩之后保留原文件
.bz2格式解压缩
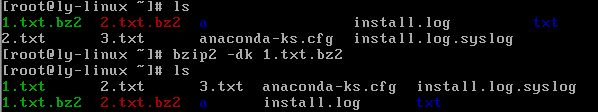
bzip2 -d 压缩文件
#解压缩,-k保留压缩文件
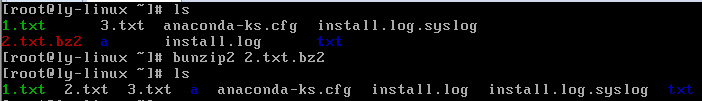
bunzip2 压缩文件
#解压缩,-k保留压缩文件
打包命令tar
#将一个目录打包成文件.tar格式,这样.gz和.bz2可压缩,解压缩目录
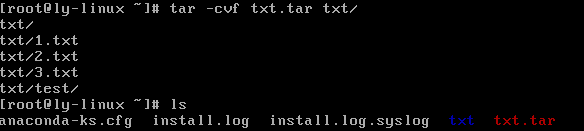
tar -cvf 打包文件名 源文件
选项:
-c:打包
-v:显示过程
-f:指定打包后的文件名
例如:tar -cvf txt.tar txt
注:打包后即可用gzip将其压缩成.tar.gz格式。
tar -xvf 打包文件名
#解打包命令
选项:
-x:解打包
例如:tar -xvf txt.tar
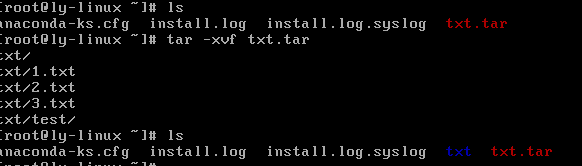
.tar.gz压缩格式
#其实.tar.gz格式是先打包成.tar格式,再压缩为.gz格式
tar -zcvf 压缩包名.tar.gz 源文件
选项:
-z:压缩为.tar.gz格式
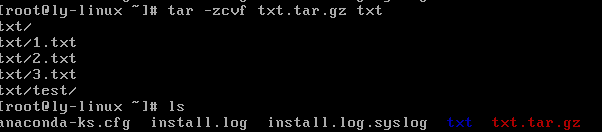
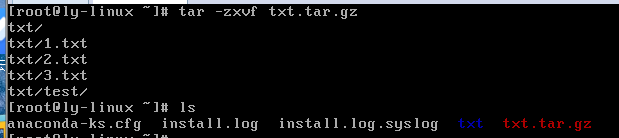
tar -zxvf 压缩包名.tar.gz
.tar.bz2压缩格式
tar -jcvf 压缩包名.tar.bz2 源文件
选项:
-z:压缩为.tar.bz2格式
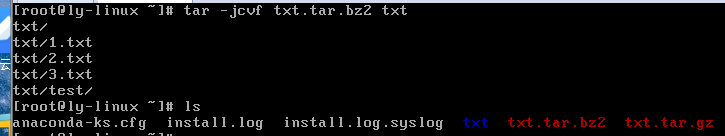
tar -jxvf 压缩包名.tar.bz2
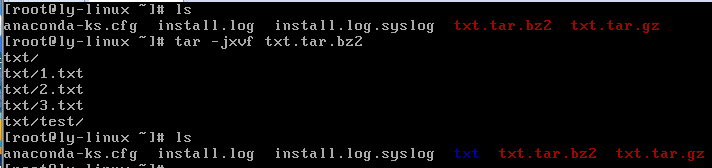
附加命令:
tar -jcvf 压缩包名.tar.bz2 源文件 源文件 。。。
#压缩多个文件,在压缩包名前加绝对路径可以指定压缩位置。
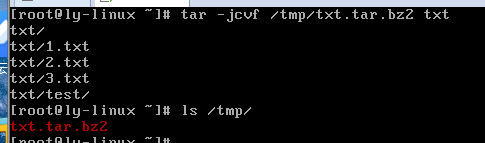
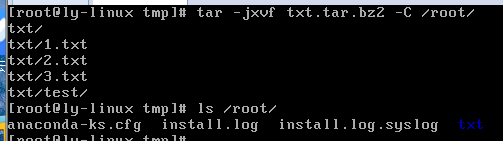
tar -jxvf 压缩包名.tar.bz2 -C 路径
#解压到指定目录,只能写在后边
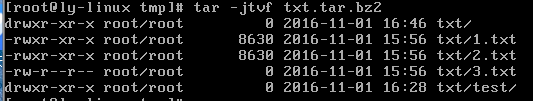
tar -jtvf 压缩包名.tar.bz2
-t:test
#只查看,不解压
#.tar.gz同理
#重点.tar.gz和.tar.bz2两种压缩格式
转载于:https://blog.51cto.com/walterliew/1882076
