源码怎么做网站南通公司建站模板
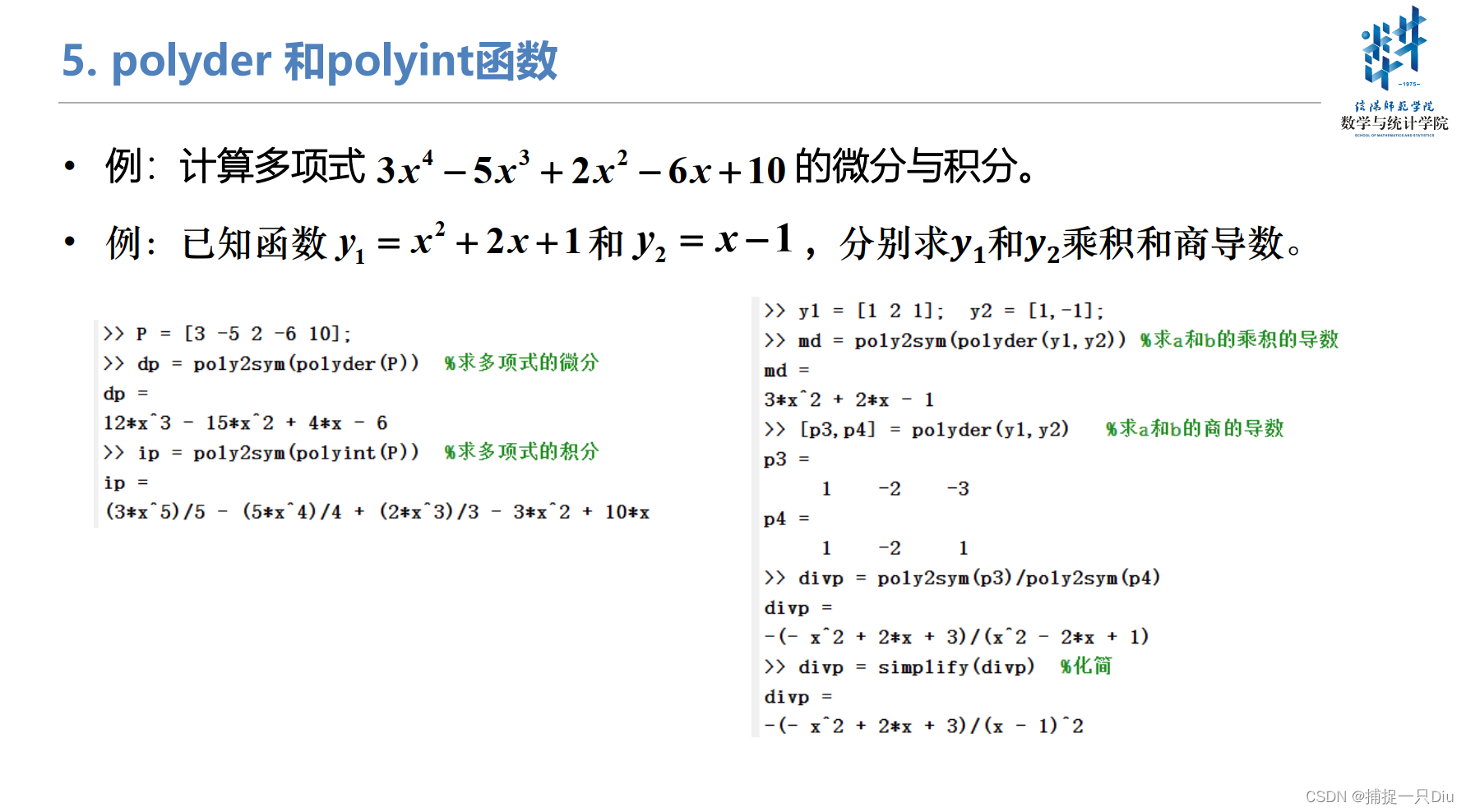
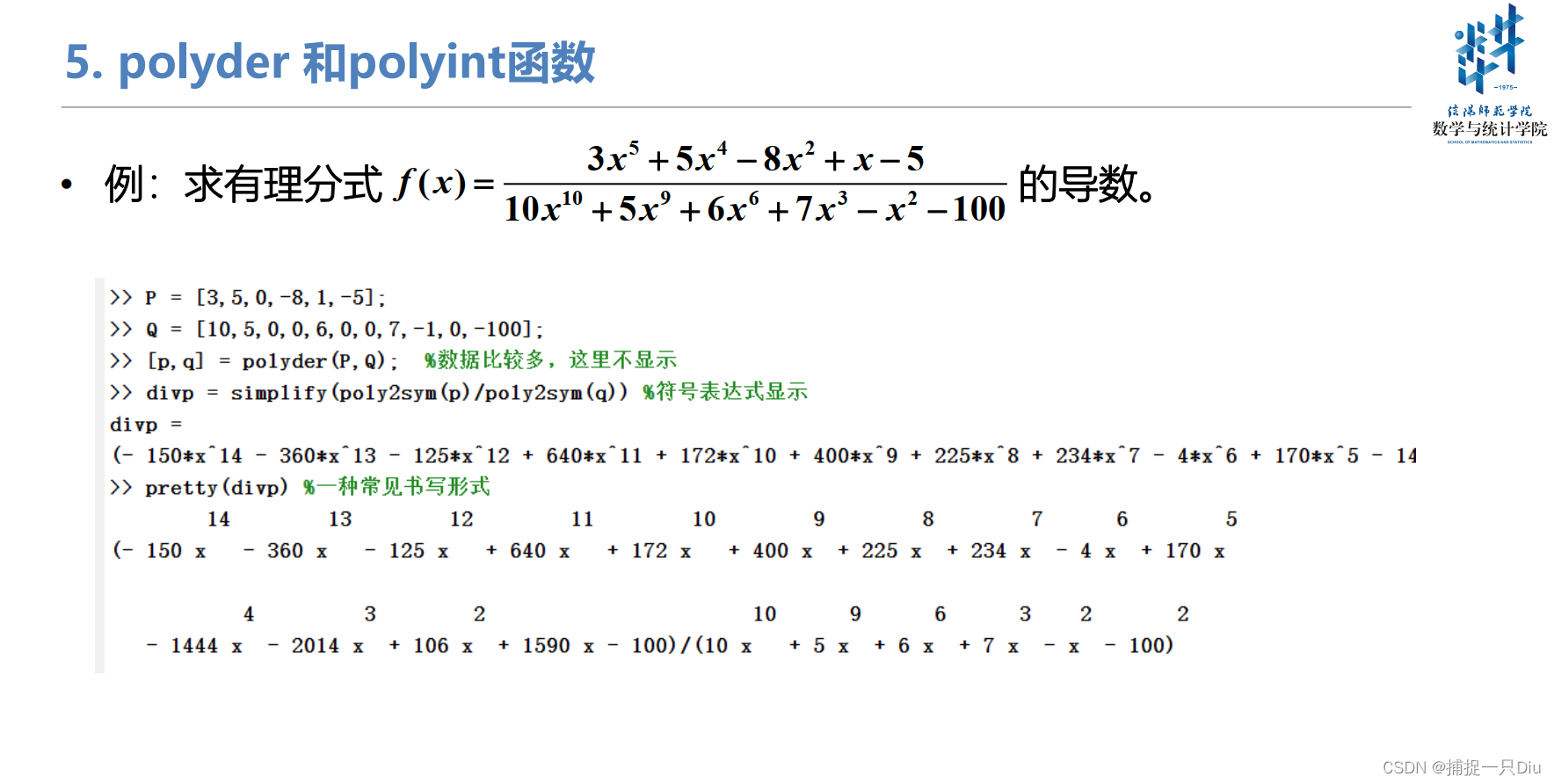
一、关于多项式的基本操作


若要求非线性方程的根,则采用fzero, fminbnd函数

二、多项式拟合
clc, clear
x=0:0.2:10; y=0.25*x+20*sin(x);
plot(x,y,'k.','MarkerSize',15)
grid on;
hold on
[p1,s1,mu1]=polyfit(x,y,3); %3阶多项式拟合
y1=polyval(p1,x,s1,mu1);
[p2,s2,mu2]=polyfit(x,y,5); %5阶多项式拟合
y2=polyval(p2,x,s2,mu2);
[p3,s3,mu3]=polyfit(x,y,8); %8阶多项式拟合
y3=polyval(p3,x,s3,mu3);
plot(x,y1,'c-', x,y2, 'r-', x,y3, 'b-');
xlabel('X');
ylabel('Y');
legend('原始数据','3阶多项式拟合', '5阶多项式拟合', '8阶多项式拟合','Location','best');
legend('boxoff')
title('不同次数拟合曲线对比图')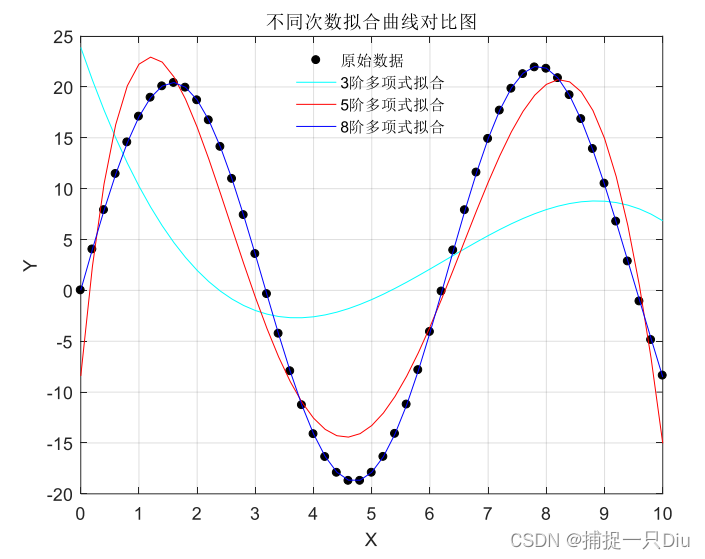
多项式评价和置信区间的估计:
clc,clear
x=0:0.2:10;
y=0.25*x+20*sin(x);
[p,s,mu]=polyfit(x,y,6); %6阶多项式拟合
[Y,DELTA] = polyconf(p,x,s,0.05,mu);
fill([x,fliplr(x)],[Y-DELTA,fliplr(Y+DELTA)],[0.95,0.899,0.9230]) %RGB
hold on
plot(x,y,'k.','MarkerSize',15)
plot(x,y,'b-')
plot(x,Y-DELTA,'m--')
plot(x,Y+DELTA,'m--')
grid on
title('6次多项式拟合及置信区间')
xlabel('X')
ylabel('Y')
曲线拟合案例分析:
clc,clear
[Data,Textdata] = xlsread('matlab视频数据\examp41.xls',1,'B3:C61');
x = 1:59;
plot(x,Data,'r.','MarkerSize',15)
% xtick坐标刻度
% numel数组元素的个数(或用length)
% xticklabel坐标显示的字符串
set(gca,'XTick',1:8:numel(x),'xticklabel',Textdata(1:8:end))
xlabel('时间')
ylabel('食品零售价格分类指数')
title('我国2007年1月至2011年11月食品零售价格分类指数数据')
x = x';hold on
[p4,s4,mu4] = polyfit(x,Data,4);
y4 = polyval(p4,x,s4,mu4);
plot(x,y4,'k:','LineWidth',1.5)[p6,s6,mu6] = polyfit(x,Data,6);
y6 = polyval(p6,x,s6,mu6);
plot(x,y4,'m--','LineWidth',1.5)[p9,s9,mu9] = polyfit(x,Data,9);
y9 = polyval(p9,x,s9,mu9);
plot(x,y9,'b.-','LineWidth',1.5)[p11,s11,mu11] = polyfit(x,Data,11);
y11 = polyval(p11,x,s11,mu11);
plot(x,y11,'g-','LineWidth',1.5)legend('原始数据','4次拟合','6次拟合','9次拟合','11次拟合');
legend('boxoff')
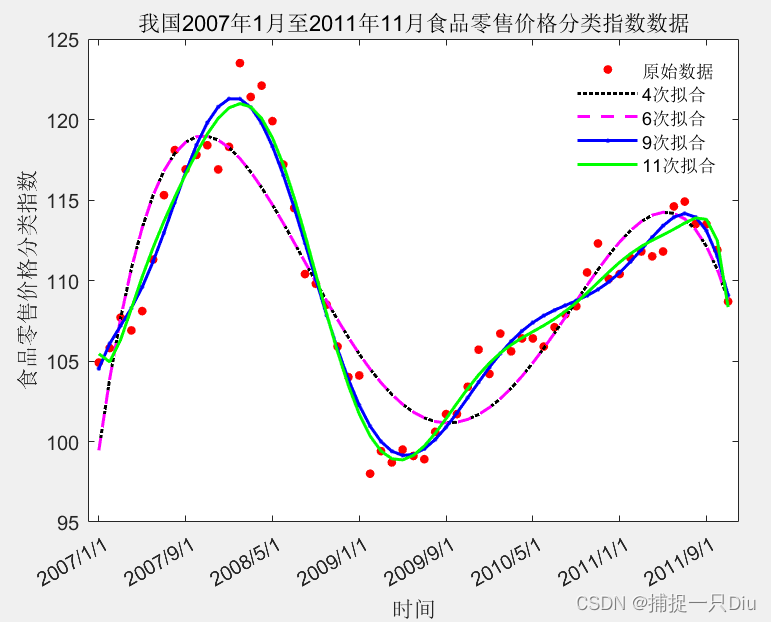
自定义函数拟合:
function y = nlinfun(beta,x)a = beta(1);b = beta(2);y = a + (0.49 - a).*exp(-b*(x-8));
endclc,clear,close
data = xlsread('matlab视频数据\nlinfit_data.xlsx');
x = data(1,:)';
y = data(2,:)';beta0 = [1,1];
beta = nlinfit(x,y,'nlinfun',beta0);
yp = nlinfun(beta,x);
plot(x,y,'r.','MarkerSize',15)
hold on
grid on
xlabel('时间T')
ylabel('氯气积分Y')
title('化工生产中氯气积分随时间下降拟合曲线')
plot(x,yp,'b-','LineWidth',2)
三、一维数据插值
一维插值函数插值方法对比:
clc,clear
x = 0:10;
y = sin(x);
xi = 0:0.1:10; %xi表示插值点
strmod = {'nearest','linear','spline','cubic'}; % 将插值方法定义为单元数组
strlb = {'(a) method = nearest', '(b) method = linear','(c) method = spline', '(d) method = cubic'}; % 将X轴标识为单元数组
for i = 1:4yi = interp1(x,y,xi,strmod{i}); %一维插值subplot(2,2,i); %生成子图plot(x,y,'ro','MarkerFaceColor','r');hold ongrid onplot(xi,yi,'b--','LineWidth',1.5)title(strlb(i)) %对每个字图添加标题
end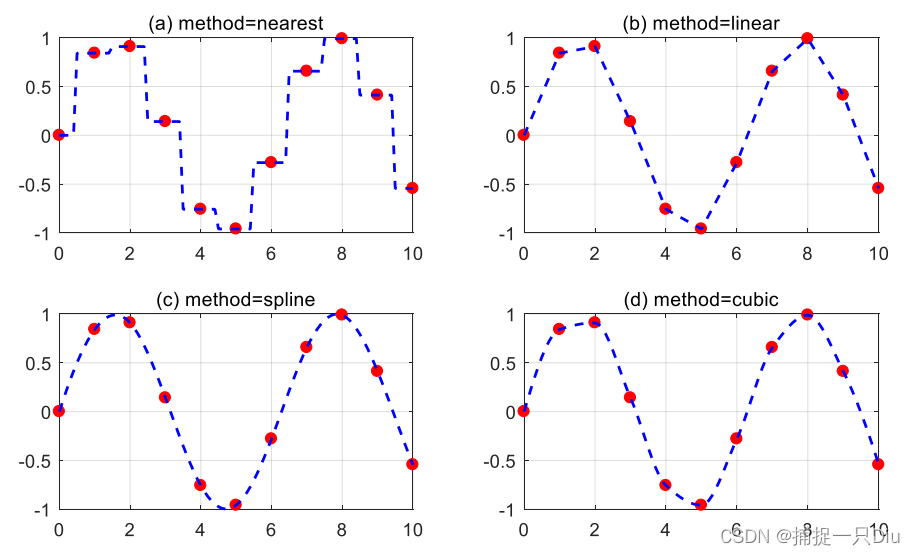
案例:环境温度数据插值

clc,clear
x = 0:2:24;
y = [12 9 9 10 18 24 28 27 25 20 18 15 13];
xi = 0:24/1440:24;yisp = spline(x,y,xi);
% P = spline(x,y);
% yisp = interp1(x,y,xi,'spline');
subplot(2,2,1)
plot(x,y,'bo',xi,yisp,'r-')
title('spline函数插值效果图')
xlabel('24时间'); ylabel('随时间温度变化值')
grid onsubplot(2,2,2)
pcs = csape(x,y,'complete') %查看三次样条插值系数矩阵
ycs = fnval(pcs,xi); %求插值
plot(x,y,'bo',xi,ycs,'r-')
title('csape函数插值效果图')
xlabel('24时间'); ylabel('随时间温度变化值')
grid onsubplot(2,2,3)
%B样条插值, k为B样条阶次,一般选择4和5
psp = spapi(4,x,y);
yspa = fnval(psp,xi);
plot(x,y,'bo',xi,yspa,'r-')
grid on
xlabel('24时间'); ylabel('随时间温度变化值')
title('spapi函数插值效果图')subplot(2,2,4)
%三次光滑样条插值, p表示光滑程度,取值[0,1]
ycsa = csaps(x,y,0.9,xi);
plot(x,y,'bo',xi,ycsa,'r-')
title('csaps函数插值效果图')
xlabel('24时间'); ylabel('随时间温度变化值')
grid on
案例:轮船甲板面积

clc,clear
x = linspace(0,8.534,13);
y = [0 0.914 5.060 7.772 8.717 9.083 9.144 9.083 8.992 8.687 7.376 2.073 0];
x0 = 0:0.001:8.534; %插值点
y1 = interp1(x,y,x0,'linear'); %线性插值
y2 = interp1(x,y,x0,'spline'); %三次样条插值
plot(x,y,'b.','Markersize',15);
hold on
plot(x0,y1,'r--',x0,y2,'g-');
S1 = trapz(y1)*0.001 %线性插值数值积分,计算梯形面积
S2 = trapz(y2)*0.001 %三次样条插值数值积分
外插估值:
% cos(10.5)外插值计算, x的区间[0.10];利用函数interp1计算10.5的函数值。
clc,clear
x = 0:0.5:10;
y = cos(x);
x1 = 10.5;
y1 = cos(x1);
y2 = interp1(x,y,x1,'nearest','extrap');
y3 = interp1(x,y,x1,'linear','extrap');
y4 = interp1(x,y,x1,'spline','extrap');
plot(x,y,x1,y1,'o',x1,y2,'>r',x1,y3,'b<',x1,y4,'r*');
legend('solution','cos(10.5)','nearest','linear','spline');
grid on
title('各种外插方法对比图')
legend('boxoff')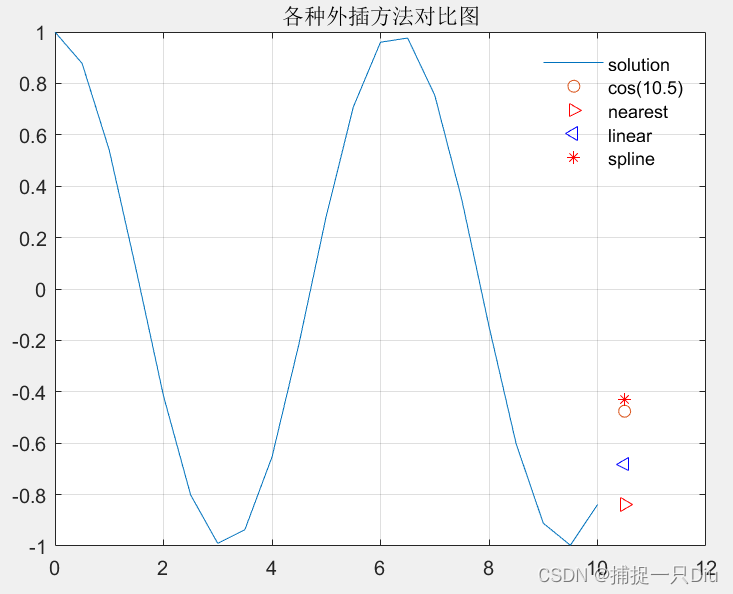
四、高维数据插值
案例:山区地貌图
% 已知某处山区地形选点测量坐标数据为:x、y和z。
clc,clear
x = 0:0.5:5; y = 0:0.5:6;
z = [89 90 87 85 92 91 96 93 90 87 82;92 96 98 99 95 91 89 86 84 82 84;96 98 95 92 90 88 85 84 83 81 85;80 81 82 89 95 96 93 92 89 86 86;82 85 87 98 99 96 97 88 85 82 83;82 85 89 94 95 93 92 91 86 84 88;88 92 93 94 95 89 87 86 83 81 92;92 96 97 98 96 93 95 84 82 81 84;85 85 81 82 80 80 81 85 90 93 95;84 86 81 98 99 98 97 96 95 84 87;80 81 85 82 83 84 87 90 95 86 88;80 82 81 84 85 86 83 82 81 80 82;87 88 89 98 99 97 96 98 94 92 87];
mesh(x,y,z) %绘制三维网格面xi = linspace(0,5,50);%加密横坐标数据到50个
yi = linspace(0,6,60);%加密纵坐标数据到60个
[xi1,yi1] = meshgrid(xi,yi);%生成网格数据
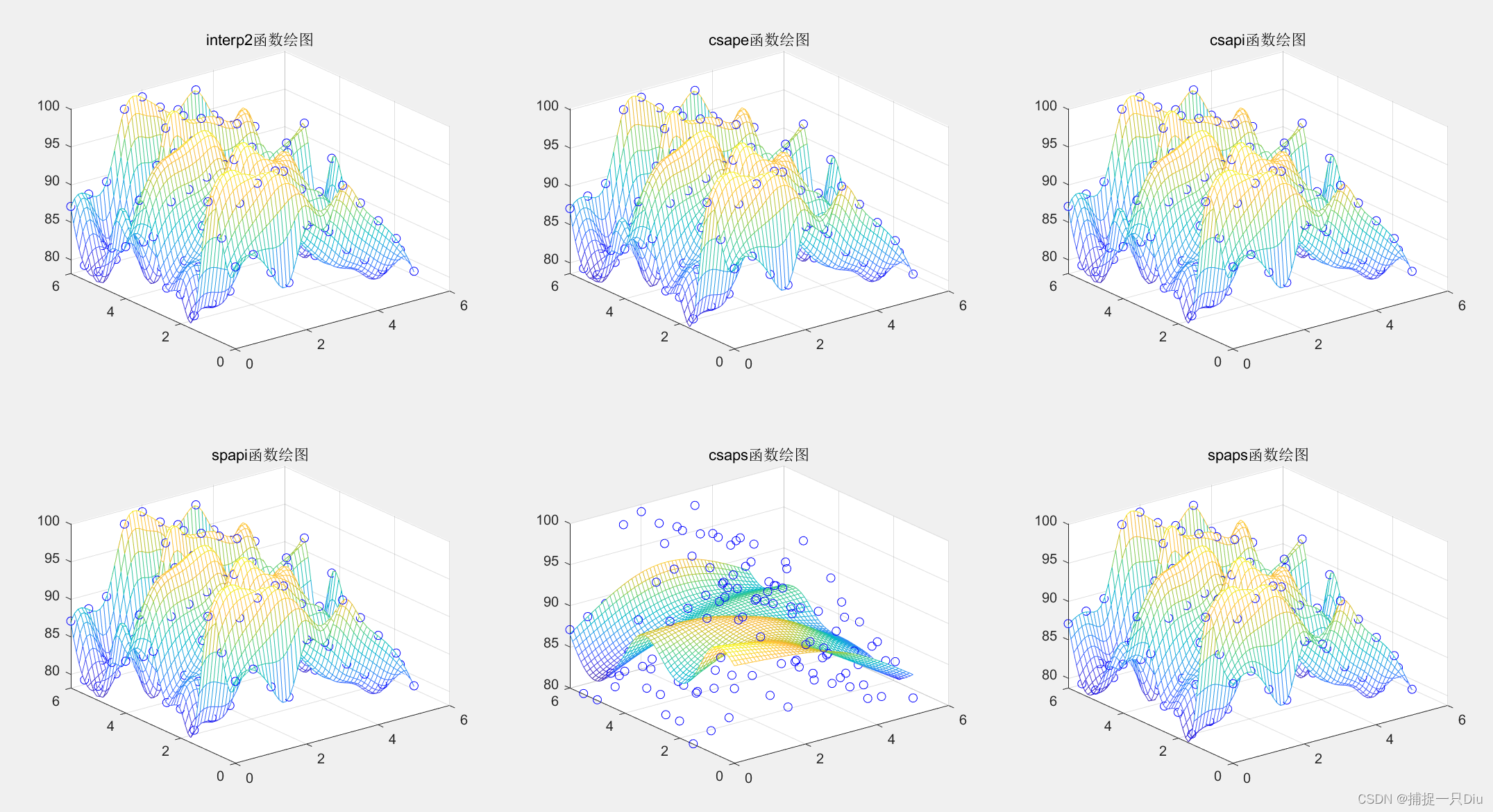
[xi2,yi2] = ndgrid(xi,yi);% ------- 调用interp2函数作三次样条插值-----------
subplot(2,3,1);
zi1 = interp2(x,y,z,xi1,yi1,'spline');
mesh(xi1,yi1,zi1);
hold on
[xx,yy] = meshgrid(x,y); %生成网格数据
plot3(xx,yy,z+0.1,'bo') %原始数据用O绘制
title('interp2函数绘图')% ------- 调用csape函数作三次样条插值----------
subplot(2,3,2);
cp1 = csape({x,y},z');
mesh(xi2,yi2,fnval(cp1,{xi,yi}));
hold on
[xx,yy] = meshgrid(x,y); %生成网格数据
plot3(xx,yy,z+0.1,'bo') %原始数据用O绘制
title('csape函数绘图')% ------调用csapi函数作三次样条插值---------
subplot(2,3,3)
zi2 = csapi({x,y},z',{xi,yi});
mesh(xi2,yi2,zi2);
hold on
[xx,yy] = meshgrid(x,y); %生成网格数据
plot3(xx,yy,z+0.1,'bo') %原始数据用O绘制
title('csapi函数绘图')% ------调用spapi函数作三次B样条插值--------
subplot(2,3,4)
sp1 = spapi({4,4},{x,y},z');
mesh(xi2,yi2,fnval(sp1,{xi,yi}))
hold on
[xx,yy] = meshgrid(x,y); %生成网格数据
plot3(xx,yy,z+0.1,'bo') %原始数据用O绘制
title('spapi函数绘图')subplot(2,3,5)
zi3 = csaps({x,y},z',{0.2,0.9},{xi,yi});
mesh(xi2,yi2,zi3);
hold on
[xx,yy] = meshgrid(x,y); %生成网格数据
plot3(xx,yy,z+0.1,'bo') %原始数据用O绘制
title('csaps函数绘图')% ---------调用spaps函数作三次B样条插值-------------
subplot(2,3,6)
sp2 = spaps({x,y},z',{1e-3,0.01});
mesh(xi2,yi2,fnval(sp2,{xi,yi}))
hold on
[xx,yy] = meshgrid(x,y); %生成网格数据
plot3(xx,yy,z+0.1,'bo') %原始数据用O绘制
title('spaps函数绘图')
散乱点插值:
案例:水道海底地貌图
clc,clear
x = [129 140 103.5 88 185.5 195 105 157.5 107.5 77 81 162 162 117.5];
y = [7.5 141.5 23 147 22.5 137.5 85.5 -6.5 -81 3 56.5 -66.5 84 -33.5];
z = -[4 8 6 8 6 8 8 9 9 8 8 9 4 9];
[cx,cy] = meshgrid(75:5:200,-90:5:150);
cz = griddata(x,y,z,cx,cy,'cubic');
figure(1)
mesh(cx,cy,cz); %绘制三维网格图
title('某水道的海底地貌图')
view(-60,30);
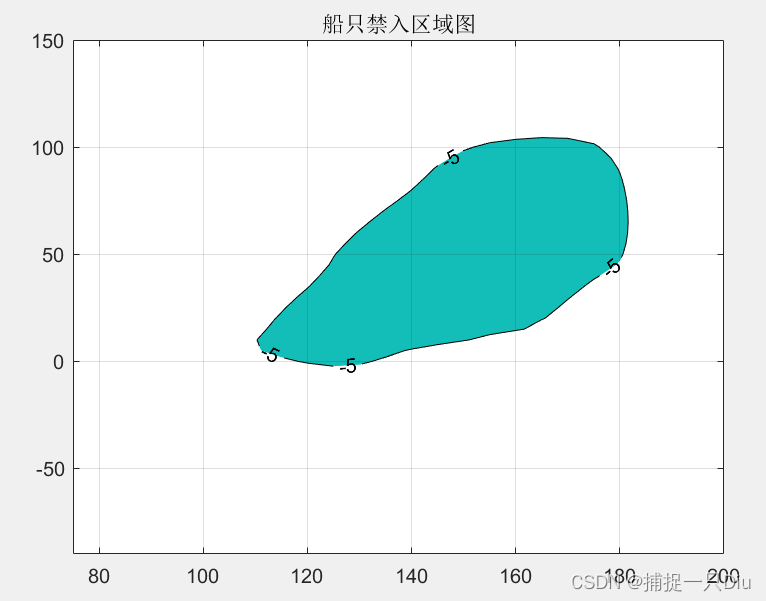
figure(2)
[c,h] = contourf(cx,cy,cz,[-5,-5],'k'); %绘制等高线
set(h,'ShowText','on')
grid on
title('船只禁入区域图')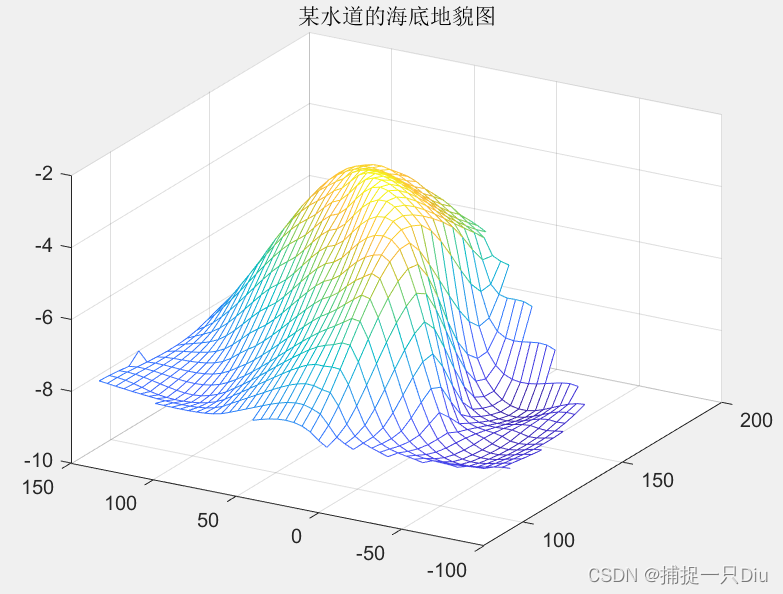
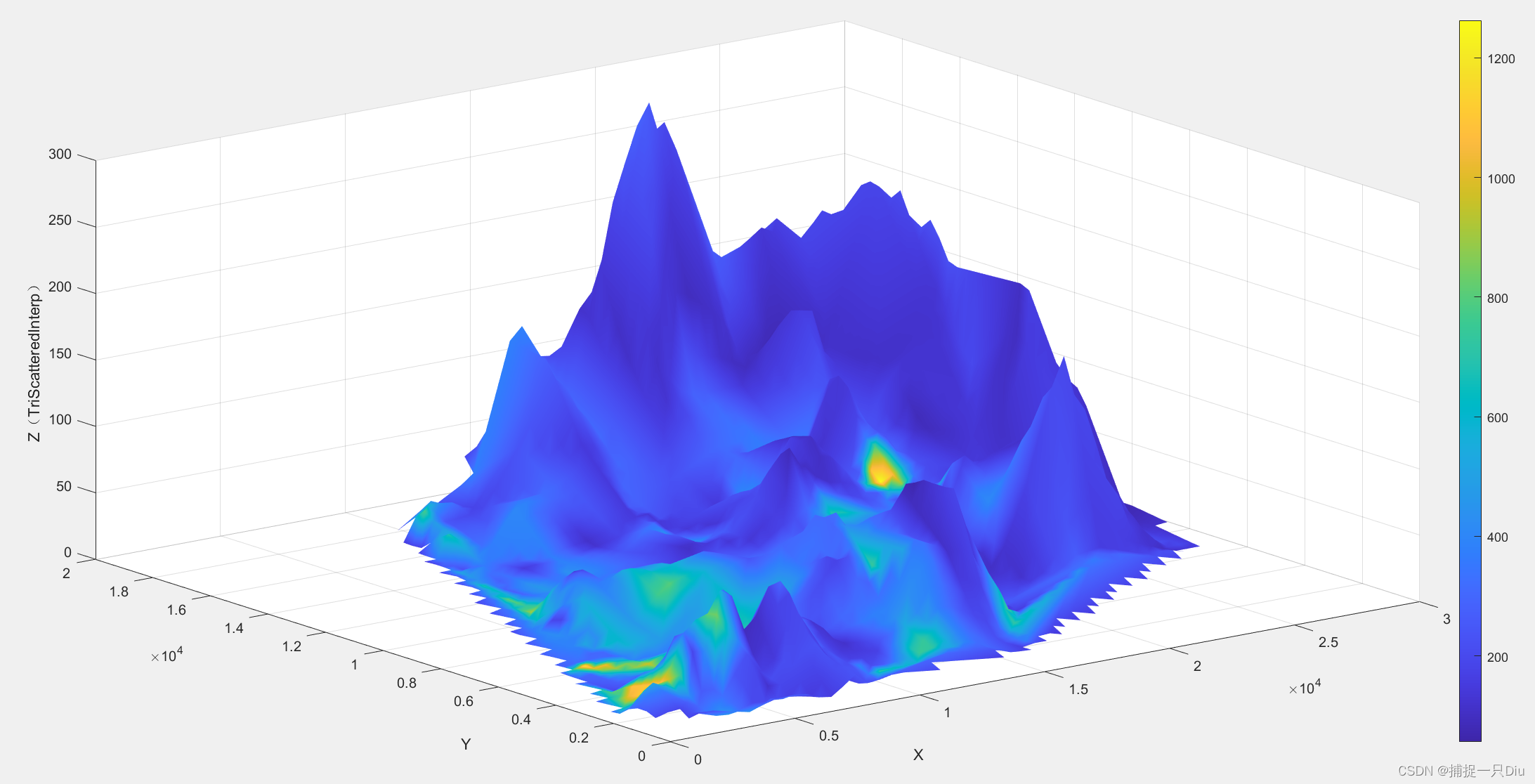
案例:城区土壤地质环境调查

clc,clear
data = xlsread('matlab视频数据\cumcm2011A.xls',1,'B4:D322');
x = data(:,1);
y = data(:,2);
z = data(:,3);
cd = xlsread('matlab视频数据\cumcm2011A.xls',2,'C4:C322');
xd = linspace(min(x),max(x),60);
yd = linspace(min(y),max(y),60);
[xi,yi] = meshgrid(xd,yd);% ------调用griddata函数作散乱节点插值-------
zi = griddata(x,y,z,xi,yi);
cdi = griddata(x,y,cd,xi,yi);
surf(xi,yi,zi,cdi) % 前三维度绘制空间曲面,第四维度用颜色表示
shading interp
xlabel('X');
ylabel('Y');
zlabel('Z(griddata)');
colorbar% ------------调用TriScatteredInterp函数作散乱节点插值------------
F = TriScatteredInterp(x,y,z);
zi2 = F(xi,yi);
Fcd = TriScatteredInterp(x,y,cd);
cdi2 = Fcd(xi,yi);
figure;
surf(xi,yi,zi2,cdi2);
shading interp;
xlabel('X');
ylabel('Y');
zlabel('Z(TriScatteredInterp)');
colorbar